Embark on a captivating exploration of worksheet elements compounds and mixtures, where we unravel the fundamental components of our universe. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of matter, distinguishing between elements, compounds, and mixtures, while shedding light on their unique properties, reactions, and applications.
From the basic building blocks of elements to the complex interactions of compounds and mixtures, this worksheet provides an in-depth understanding of the chemical world around us.
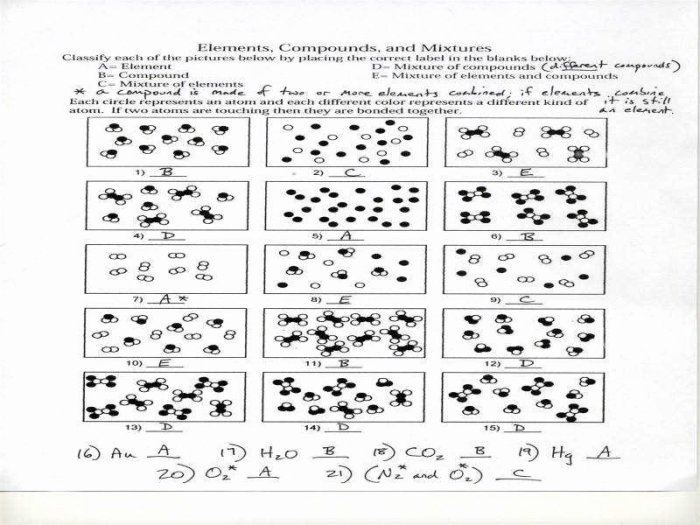
1. Worksheet Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
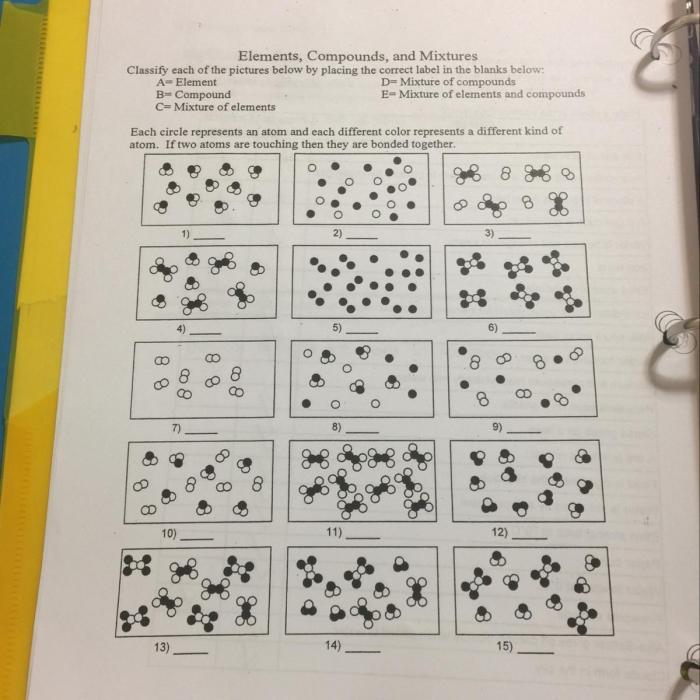
This worksheet introduces the concepts of elements, compounds, and mixtures, providing examples and describing methods for their separation.
Elements
- Pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means
- Examples: gold, oxygen, hydrogen
Compounds
- Substances composed of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions
- Examples: water (H 2O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), sodium chloride (NaCl)
Mixtures
- Combinations of two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded
- Examples: air (mixture of gases), salt water (mixture of water and salt), granite (mixture of minerals)
Separation of Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
- Physical methods: filtration, distillation, chromatography
- Chemical methods: electrolysis, reactions
2. Properties of Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Physical Properties
Elements
- Unique melting and boiling points
- Can be solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature
- Exhibit specific colors, densities, and electrical conductivities
Compounds
- Fixed melting and boiling points
- Can be solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature
- Exhibit unique properties based on the elements they contain
Mixtures
- Variable melting and boiling points
- Can be solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature
- Properties vary depending on the composition and proportions of components
Chemical Properties
Elements
- React with specific elements in predictable ways
- Can undergo oxidation, reduction, and other chemical reactions
- Form compounds with other elements
Compounds
- React with specific compounds or elements in predictable ways
- Undergo chemical reactions to form new compounds
- Properties depend on the elements they contain
Mixtures
- Do not undergo chemical reactions
- Components retain their individual properties
- Can be separated by physical means
3. Reactions of Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Types of Reactions
Elements
- Combine to form compounds
- React with compounds to form new compounds
- Undergo oxidation-reduction reactions
Compounds
- React with elements to form new compounds
- React with other compounds to form new compounds
- Undergo decomposition reactions to form elements or simpler compounds
Mixtures
- Do not undergo chemical reactions
- Components retain their individual properties
Comparison of Reactions
- Elements: undergo chemical reactions to form new substances
- Compounds: undergo chemical reactions to form new substances or decompose into simpler substances
- Mixtures: do not undergo chemical reactions
4. Applications of Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures: Worksheet Elements Compounds And Mixtures
Applications of Elements
- Gold: jewelry, electronics, dentistry
- Oxygen: breathing, medical applications, industrial processes
- Hydrogen: fuel, rocket propulsion, chemical reactions
Applications of Compounds
- Water (H 2O): essential for life, drinking, agriculture, industry
- Carbon dioxide (CO 2): fire extinguishers, carbonated beverages, photosynthesis
- Sodium chloride (NaCl): table salt, food preservation, chemical processes
Applications of Mixtures
- Air: essential for life, respiration, combustion
- Salt water: oceans, seas, lakes, food preservation
- Granite: building materials, countertops, monuments
Comparison of Applications, Worksheet elements compounds and mixtures
- Elements: used in various industries and applications
- Compounds: essential for life, used in a wide range of products and processes
- Mixtures: found in nature and used in various applications, often for their unique properties
Helpful Answers
What is the difference between an element and a compound?
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, while a compound is a substance composed of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions.
How can you separate a mixture?
Mixtures can be separated based on the different physical properties of their components, such as filtration, distillation, or chromatography.
What are the applications of elements in everyday life?
Elements have a wide range of applications, including construction (iron), energy production (uranium), and electronics (silicon).
